The Rise of Smart Homes
The idea of "smart homes" was made possible by technological advancements, which have completely changed the way that household appliances and consumer gadgets are sold. This section examines the development and current developments in smart home technology, considering the ways in which they have changed how we use and interact with our living environments.
Evolution and Current Trends in Smart Home Technology
Evolution: The history of smart homes started with simple automated systems, such as garage door openers and alarm systems, that were mainly utilized for security and simple job automation. With the introduction of the Internet of Things (IoT), which allows for improved device connectivity and interaction, the progression has quickened. As a result of this advancement, integrated home automation systems with controls for the lighting, HVAC, and entertainment systems have been made possible.
Current Trends: In terms of consumer electronics innovation, smart home technology is leading the way now. The current trends center on improving security, energy efficiency, and user ease. With the advent of machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI), smart home systems now have the capacity to learn from and adjust to user preferences and habits, providing individualized experiences.
- Home Automation Platforms: By integrating with a wide range of sensors, including motion detectors and temperature sensors, smart home platforms like Google Home, Amazon Alexa, and Apple HomeKit enable accurate monitoring and control over numerous aspects of the home environment. Through voice commands or smartphone applications, these platforms enable users to monitor and manage appliances, lighting, thermostats, and security systems within their homes. By using sensor data, these platforms provide real-time feedback and modifications.
- Energy Management: With the use of cutting-edge sensor technology and real-time data processing, users can effectively monitor and optimize their energy consumption, thereby promoting environmental sustainability.
- Security and Surveillance: By offering real-time alerts and remote monitoring capabilities, enhanced security systems with motion detectors, cameras, and smart locks give users peace of mind.
- Health and Wellness: To ensure a healthy living environment, smart homes include health and wellness features. These features make use of sensors and equipment that keep an eye on temperature, humidity, and air quality.
- Integration and Interoperability: Users may now build a harmonious and cohesive smart home ecosystem by integrating and integrating different smart devices seamlessly, thanks to an ongoing trend in this direction.
The development of sensor technologies, which provide the fundamental building blocks for gathering real-world data, has been closely linked to the creation of smart home technology. Our living spaces are now networked ecosystems that not only adapt to our wants and preferences but also continuously collect and process sensor data to improve those responses. These developments in automation, networking, and user interfaces have made this possible. The latest developments in smart home technology, which are driven by ever-more-advanced sensors, point to a future in which our houses will be more intelligent, sustainable, and personalized. They also herald a move towards more security and personalization.
Wearable Devices
The consumer electronics industry has been significantly impacted by the widespread use of wearable technology. With a specific focus on health monitoring employing bio-sensors, motion tracking, and environment sensing, these small, easy-to-use devices are revolutionizing health monitoring and providing creative ways to incorporate technology into our daily lives.
Health Monitoring Using Bio-Sensors, Motion Tracking, and Environment Sensing
Bio-Sensors: Integrated into wearable technology, bio-sensors play a critical role in health monitoring by helping to track physiological factors, including heart rate, oxygen saturation, and glucose levels, in real time. By offering insightful information on the user's health, these sensors help preventative health care and enable early identification of possible problems.
Motion Tracking: Motion tracking technology, found in wearables like gyroscopes and accelerometers, tracks fitness data like steps taken, distance traveled, and calories burned while monitoring physical activity. This function is helpful for users who want to lead active lifestyles since it provides encouragement and feedback to help them reach their fitness objectives.
Environment Sensing: The ability to sense the environment, including UV exposure, air quality, and ambient temperature, is becoming more and more integrated into wearable technology. These features help people make well-informed decisions to reduce environmental health risks and enhance general well-being.
Battery Management: Devices such as fitness trackers, smartwatches, and medical wearables use low-power current sensors with a small footprint to measure current consumption for efficient battery management.
Applications and Implications
Preventive Healthcare: The incorporation of health monitoring technologies into wearables, which enable users to continuously monitor their lifestyle choices and vital signs, makes preventive healthcare possible. This aids in the early detection and treatment of health issues.
Personalized Health Insights: Wearable technology's analytical powers enable users to get tailored health insights and advice, enabling them to make educated decisions about their lifestyle and well-being.
Enhanced User Experience: By providing a comprehensive method of tracking health and wellness, the combination of biosensors, motion tracking, and environment sensing technologies in wearables improves the user experience.
Research and Development: Extensive research and development activities are driving the ongoing growth of wearable technology, with the goal of broadening the wearables' application spectrum and investigating novel approaches to health monitoring and management.
With their innovative health monitoring solutions that combine state-of-the-art technology and user-centric design, wearable gadgets mark a significant development in consumer electronics. Wearable technology that incorporates biosensors, motion tracking, and environmental sensing offers a comprehensive approach to health monitoring. This helps users better understand their surroundings and personal health, and it also paves the way for a society that is healthier and more knowledgeable.
Entertainment Systems
Modern consumer electronics would not be complete without entertainment systems, which combine creativity and technology to create immersive experiences. With the introduction of cutting-edge features like gesture control, touchscreens, and ambient light sensors, the entertainment system market has completely changed, improving consumer engagement and interactivity.
Touchscreens, Gesture Control, Ambient Light Sensing
Touchscreens: The development of user interfaces that are responsive and intuitive depends heavily on touchscreen technology. This technology offers a seamless user experience by doing away with the requirement for conventional input devices by enabling direct connection with the display. It greatly affects user engagement and content navigation and is extensively integrated into a wide range of devices, including interactive kiosks, tablets, and smartphones.
Gesture Control: This technology uses motion and position to recognize and understand human gestures, allowing users to interact with devices. Particularly in gaming consoles and smart TVs, where gesture detection allows users to explore and control the system intuitively without the need for conventional remote controls or buttons, this type of interaction delivers a more natural and immersive user experience.
Ambient Light Sensing: In order to adjust the display brightness to the ambient light, ambient light sensors are essential. These sensors automatically change the screen's brightness, which improves viewing quality and extends the battery life of portable devices while also promoting energy efficiency.
Innovation and Integration
Enhanced User Engagement: In particular in gaming and multimedia applications, the combination of touchscreens, gesture control, and ambient light sensor technologies greatly increases user engagement by creating immersive and interactive worlds.
Accessibility: New developments in entertainment system technology have made it possible for users of all ages and abilities to interact with more intuitive and user-friendly interfaces, creating new avenues for accessibility.
Customized User Experience: By combining these cutting-edge technologies, consumers can engage with gadgets and information in ways that best suit their requirements and preferences.
Energy Efficiency: As a key component of sustainability and longer device lifespan, energy efficiency is continuously optimized in these technologies.
With the integration of technologies like gesture control, touchscreens, and ambient light sensors, entertainment systems have experienced a revolutionary transformation that has redefined user engagement and experience. With user-centric solutions that address accessibility and energy efficiency while also meeting the changing demands and tastes of the modern consumer, these innovations highlight the immersive and interactive components of entertainment.
Kitchen and Laundry Applications
In today's world, it is essential to integrate technology with conventional appliances in order to maintain a fast-paced lifestyle. The combination of temperature controls, moisture sensors, and energy consumption monitors has led to significant breakthroughs in kitchen and laundry applications, namely improving efficiency, convenience, and sustainability.
Moisture Sensors, Temperature Controls, Energy Consumption Monitors
Moisture Sensors: For optimum performance and energy efficiency, moisture sensors are essential in kitchen and laundry appliances, such as dryers and dishwashers. These sensors minimize water and energy waste by detecting the moisture content of the appliance and adjusting the operation accordingly, preventing over-drying or over-washing and extending the life of clothes and utensils.
Temperature Controls: Accurate temperature controls are essential for washing machines, stoves, and freezers. By enabling customers to choose precise temperatures, they guarantee ideal conditions for cooking, preserving, and washing. Sophisticated temperature control systems protect food quality and textile integrity while increasing energy efficiency by strictly maintaining the required temperature through the use of sensors and micro-controllers.
Energy Consumption Monitors: Keeping an eye on energy usage is essential to the economical and environmentally responsible operation of household appliances. Refrigerators and washing machines, for example, have integrated energy monitors that give customers immediate data on energy usage. This allows users to better control their energy use and make decisions that will lower their energy costs and environmental effects.
Enhancements and Implications
Optimization and Efficiency: By integrating cutting-edge sensors and controls, appliances may function at peak efficiency, saving energy and improving the effectiveness of household tasks as a whole.
User Convenience: Modern kitchen and laundry appliances with sophisticated controls and monitoring systems make it easier for users to interact with the appliances, enabling more intuitive control and monitoring of their operations. This saves time and effort when performing household chores.
Sustainability: By reducing energy waste and encouraging responsible energy usage, energy monitors and improved controls help to promote sustainability and are in line with international efforts to slow down environmental degradation.
Smart Integration: By combining these technologies with smart home systems, customers may monitor and manage their appliances from a distance, improving convenience and facilitating proactive task management.
A notable advancement in consumer electronics is the incorporation of temperature controls, energy consumption monitors, and moisture sensors in kitchen and laundry applications. In addition to improving home appliance performance and efficiency, these developments also bring previously unheard-of convenience and support sustainability. The careful blending of these technologies highlights user-centric innovation and ethical consumption while reflecting the changing demands and tastes of the modern consumer.
Case Study: The Journey of a Smartphone – Integrating Multiple Sensors for a Seamless Experience
The smartphone, which uses a variety of sensors to improve performance and user experience, is the pinnacle of consumer electronics engineering. This case study clarifies how several sensors are integrated into cell phones, offering insights into the complex synergy that drives smooth user interactions and a wide range of applications.
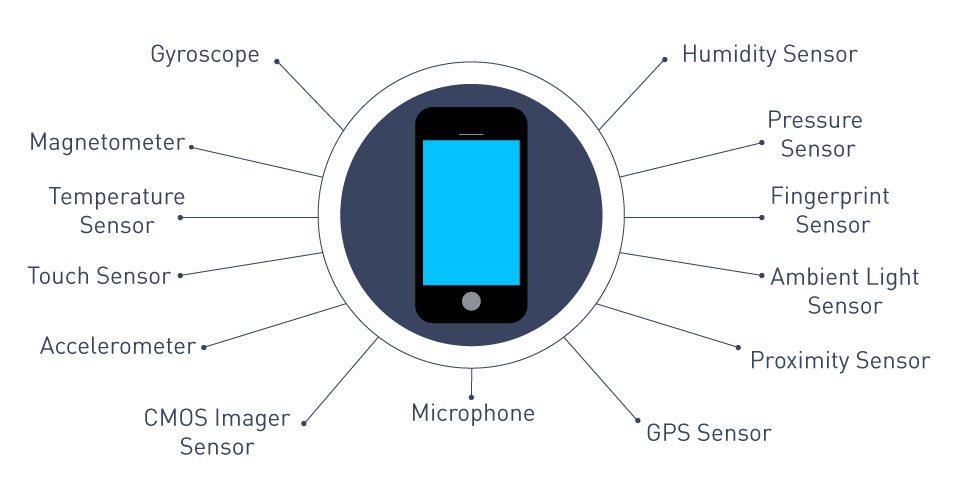
Figure 1: Smartphone Sensors
Integration of Multiple Sensors
A variety of sensors are present in modern smartphones, each having a specific function that they all work together to seamlessly and intuitively support. Among the integrated sensors are:
Accelerometers and Gyroscopes: These sensors make it possible to determine the orientation and movement of the phone, which is essential for applications that measure fitness, play games, and navigate.
Proximity Sensors: Proximity sensors are essential for dimming the screen and turning off touch during calls when the device is near the user's face since they can identify the presence of things without making physical contact.
Ambient Light Sensors: These sensors balance power usage and visibility by automatically adjusting screen brightness in real time to the ambient light.
Camera Sensors: Advanced camera sensors produce high-quality pictures and films. They are supplemented by other sensors, such as depth sensors, to provide better photography and augmented reality applications.
Biometric Sensors: Facial recognition and fingerprint sensors strengthen device security by offering quick and safe ways to authenticate users.
Environmental Sensors: A few smartphones come with sensors that track things like humidity, temperature, and air quality. These sensors provide important data about the environment that may be used to improve one’s health and well-being.
Challenges and Breakthroughs
Challenges
- Miniaturization and Integration: Getting a large number of sensors to work together in the small space of a smartphone presents a number of difficulties that need constant innovation in sensor miniaturization and integration methods.
- Power Consumption: In order to extend battery life, energy-efficient sensors and power management techniques must be developed. Operating several sensors requires a significant amount of energy.
- Calibration and Accuracy: It is crucial to guarantee the precision and dependability of sensor readings, which calls for exact calibration and sophisticated algorithms to analyze sensor data.
Breakthroughs
- Advanced Manufacturing Techniques: Manufacturing innovations have made it possible to produce sensors that are smaller, more dependable, and more efficient. This has made it possible to integrate a variety of sensors into tiny smartphone form factors.
- AI and Machine Learning: By utilizing AI and machine learning algorithms, sensor data may be interpreted and applied more effectively, leading to more intelligent, responsive, and customized user experiences.
- Enhanced Sensor Technologies: As a result of ongoing progress in sensor technology, a greater range of applications and an improved user experience may be reaped from increasingly accurate and adaptable sensors.
The integration of numerous sensors in smartphones is an illustration of how various engineering fields come together to create a seamless and varied user experience. The constant quest for perfection in consumer electronics engineering is highlighted by the ongoing advancements in sensor technology, integration strategies, and data interpretation approaches. The smartphone, with its array of built-in sensors, is a living example of the creative possibilities of engineering and how technology can improve people's lives.








直接登录
创建新帐号