Evolution from Optocouplers to Digital Isolators
In the realm of electrical isolation technology, the progression from optocouplers to digital isolators signifies a substantial evolution. The advancements in semiconductor technology, material science, and the evolving demands of modern electronic systems for higher performance and integration are depicted by this transition.
The Era of Optocouplers
Origins and Functionality: Emerging as a solution to isolate electronic circuits while facilitating signal transmission, optocouplers, or optoisolators, serve for both analog and digital isolation. Utilizing light for signal transmission across an isolation barrier, optocouplers commonly incorporate a light-emitting diode (LED) as the transmitter and a photodiode as the receiver. Alternatively, designs may employ an infrared light-emitting diode (IR LED) as the transmitter and a phototransistor as the receiver.
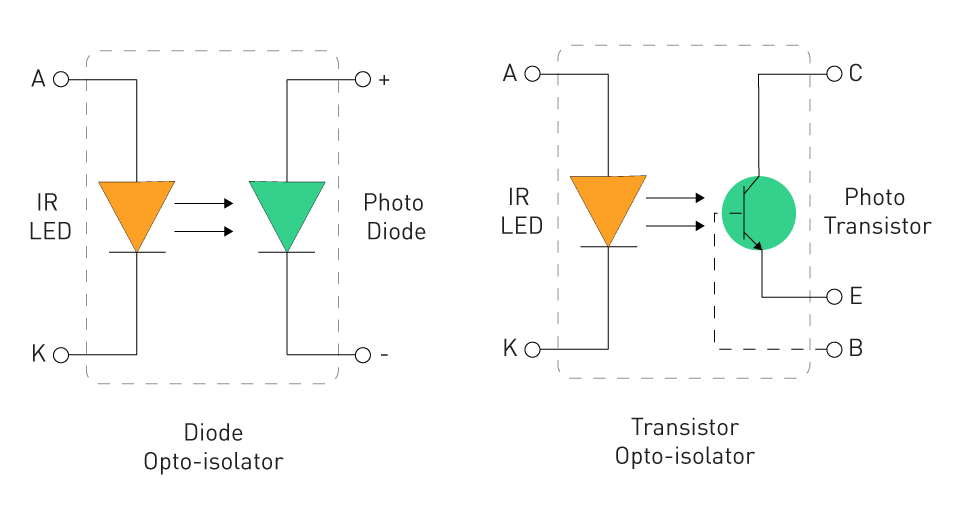
Figure 1: Types of Optoisolators
Early Adoption: With their invention dating back to 1963, optocouplers emerged as a prevalent isolation solution in numerous electronic applications, appreciated for their simplicity and effective isolation capabilities.
Limitations of Optocouplers
Speed Constraints: Primarily due to the relatively slow response time of the LED and phototransistor components, Optocouplers are limited in their data transfer rate.
Aging and Degradation: Over time, the LED component within optocouplers may degrade, resulting in alterations in performance and a decrease in the device's effective lifespan.
Power Efficiency: Due to the energy needed to drive the LEDs, optocouplers suffer from lower power efficiency.
Unidirectional: Data transfer through optocouplers is unidirectional.
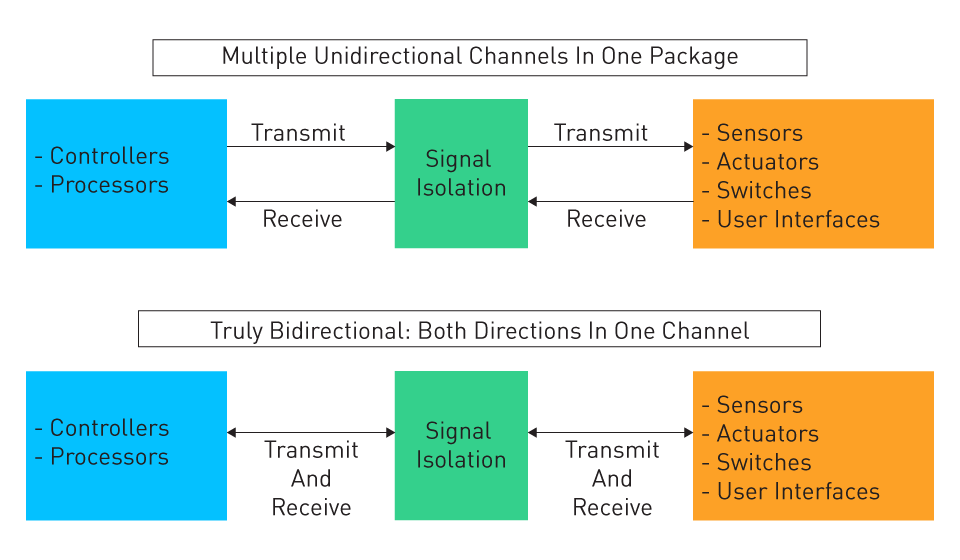
Figure 2: Unidirectional vs. Bidirectional Isolation
Limited Integration and Size: Miniaturization and high-density integration faced challenges due to the physical size and discrete nature of optocouplers, especially in space-constrained applications.
Advent of Digital Isolators
Technological Innovations: Advancements in silicon-based complementary metallic oxide semiconductor (CMOS) fabrication techniques stimulated the development of digital isolators. This progress was fueled by the demand for faster and more dependable isolation solutions.
Functionality: Advanced semiconductor technologies like capacitive or magnetic coupling have been used by digital isolators to transmit signals, enabling lower power consumption, higher data rates, and greater integration.
Performance and Integration Advantages
Higher Data Rates: In comparison with optocouplers, digital isolators offer crucially higher data transmission speeds, majorly because of better switching features, and demand for high-speed digital communication. In contrast to optoisolators, digital isolators have lower rise and fall times and much lower propagation delay.
Improved Reliability and Longevity: Digital isolators show more stable performance over their lifespan with no LED to degrade over time.
Compactness and System Integration: Leveraging CMOS semiconductor technology, digital isolators attain a more compact form, facilitating their integration into integrated circuits (ICs) and promoting miniaturization in electronic design.
Impact on Modern Electronics
Widening Applications: Expanding their utilization across various domains, digital isolators found applications in medical equipment, renewable energy systems, industrial automation, and automotive electronics.
Driving Innovation: Continued innovation in isolation technology has been fueled by the transition to digital isolators. Research and development efforts persistently aim to reduce power consumption, enhance efficiency, and improve integration capabilities.
Milestones in Digital Isolation Technology
Throughout digital isolation technology, many pivotal milestones have significantly propelled the field forward. These milestones trace the technology's progression from its initial stages to the intricate digital isolators employed in contemporary applications.
Invention of the Optocoupler (1960s): In the 1960s, the inception of the initial optocouplers marked the dawn of modern electrical isolation technology. By utilizing light for signal transmission and electrical isolation, these devices pioneered a breakthrough in the safe management of electrical circuits.
Introduction of High-Speed Optocouplers (1980s): The development of high-speed optocouplers in the 1980s stemmed from advancements in optoelectronics. Faster data transmission rates were provided by these devices, thus unlocking new possibilities in telecommunications and data processing. Today, modern high-speed optocouplers can sustain maximum data rates of up to 50 Mbps.
Emergence of Semiconductor-Based Isolation (Late 1990s): Semiconductor-based isolation methods began to emerge in the late 1990s. In contrast to optocouplers, these technologies (capacitive and magnetic coupling) improved speed, reliability, and integration by not relying on optical components. Data rates beyond 100 Mbps are supported by modern capacitive optocouplers.
Development of Integrated Isolation (Early 2000s): Integrated isolation technologies began to emerge in the early 2000s, characterized by the embedding of isolation functionality directly within semiconductor chips. This integration facilitated more streamlined designs and enhanced the capability of individual chips to accommodate greater functionality within a singular unit.
Giant Magneto-Resistance (GMR) Based Digital Isolators: The development of Giant Magneto-Resistance (GMR) based digital isolators marks a critical milestone in the evolution of digital isolation technology. To transfer data across an isolation barrier, these isolators use the GMR effect, which is a quantum mechanical phenomenon discovered in the late 1980s. Highly valued for their exceptional data transfer rates and minimal power consumption, GMR isolators have emerged as pivotal components in the progression of digital isolation. They have a crucial role, particularly in applications requiring high-speed operation and low-energy footprints. Significantly broadening the scope and capabilities of digital isolation solutions, these isolators represent a leap forward from traditional optocoupler technologies.
Illustrating a dynamic and rapidly evolving field, the milestones in digital isolation technology span from the inception of the optocoupler to the latest advancements in integrated isolators. Each development has progressively expanded the capabilities and applications of these essential components. With ongoing technological advancements, digital isolators are anticipated to play an increasingly integral role in a diverse array of electronic systems, fostering innovation in system design and electrical isolation.





直接登录
创建新帐号