Definition and Purpose of Standby Power Systems
Designed to keep the lights on in the event of a power outage, standby power systems are an integral part of today's infrastructure. These systems play a key role in ensuring that critical activities and safety measures are not jeopardized during power outages by maintaining the continuity of electrical supply in critical conditions.
Definition of Standby Power Systems
The term "standby power system" can refer to either an emergency power system or a system that uses a mix of generators and batteries to automatically provide electricity when:
- The electrical grid, which serves as the primary source of power, fails, or
- Problems with power quality, including overvoltages, undervoltages, frequency mismatches, and phase loss, affect the primary power supply.
Under regular circumstances, these systems are dormant. In the event of a power outage, certain backup power systems, such as generators, are set into motion by means of an automated transfer switch.
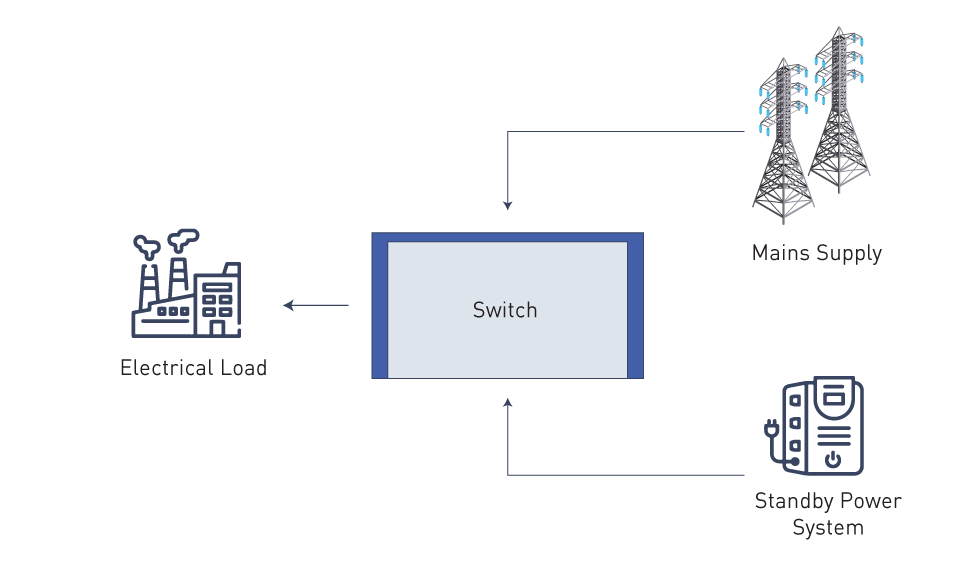
Figure 1: Standby power system concept
Purpose of Standby Power Systems
Standby power systems ensure reliability and safety in settings where major failures, financial losses, or health and safety issues could result from power disruptions. Important functions include:
Continuity of Critical Operations: For uninterrupted patient care, data integrity, and ongoing production operations, critical machinery and computer systems must be able to rely on standby power systems in hospitals, data centers, and industrial sites.
Safety Measures: Fire alarms, emergency lights, and smoke evacuation systems are all examples of crucial safety systems that rely on standby power to keep occupants safe in the event of a power outage.
Prevention of Data Loss: In the fields of information technology and telecommunications, these systems guarantee that servers and networks are always up and running, protecting against data loss and hardware damage that might happen due to improper system shutdown.
Types of Standby Power Systems
Generators: The most typical form of backup power is a generator, which can run a building or facility for long periods of time until the main power supply goes back online. These generators are usually powered by diesel, natural gas, or propane.
Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS): These systems offer rapid power, typically from batteries, to mitigate the immediate impact of power outages. They are frequently used by computer systems and other delicate electrical devices.
Battery Systems: Facilities seeking to integrate more sustainable practices into their standby power strategy now have the option of larger battery installations, which can support big loads for extended durations.
Integration with Renewable Energy
Battery storage is becoming an integral part of modern backup power systems, which also incorporate renewable energy sources like wind turbines and solar panels. This integration provides a more dependable and cost-effective method of managing power redundancy, while also enhancing the sustainability of emergency power solutions.
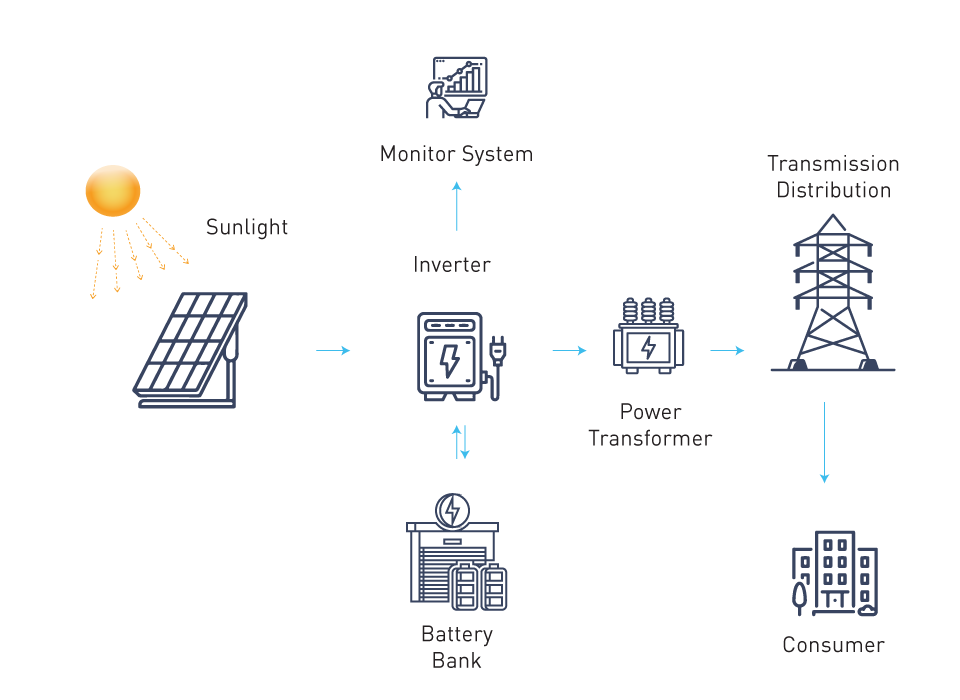
Figure 2: Grid-tied solar array
Importance of Standby Power in Ensuring Continuity of Operations
Modern infrastructure would be incomplete without standby power systems, which are essential for the smooth operation of many different industries. In high-priority locations where serious operational disruptions, safety risks, or financial losses could result from power outages, these systems are of the utmost importance.
Ensuring Operational Continuity
Standby power's capacity to keep operations running smoothly is its principal value. For what it's worth, this is paramount:
Healthcare Facilities: Maintaining sterile conditions, running life-saving machinery, and managing patient data systems all depend on healthcare facilities having reliable power. Critical biological components, including medications, blood, tissues, and organs, necessitate refrigeration, making standby power an absolute necessity for patient care.
Data Centers: Enterprise operations, cloud storage services, and online platforms in the digital age rely on data centers. Standby power solutions protect millions of users from potential data loss and service outages, guaranteeing data integrity and continuous service availability.
Emergency Services: Fire stations, police stations, and rescue services rely on uninterrupted power supplies to carry out their emergency response activities. In the event of a power loss, standby power systems keep essential services running, such as communication and emergency lighting.
Industrial and Manufacturing Sectors: In the manufacturing and industrial sectors, power outages can halt output, damage machinery, and erase unsaved data because many industrial processes are very sensitive to them. The presence of standby power, which offers an instant backup power supply, helps to reduce the impact of these risks.
Risk Management
Standby power systems are an important part of risk management plans in areas that are vulerable to natural disasters such as hurricanes, earthquakes, and floods, which can cut out the main power supply . The ability to access backup power is crucial for ensuring a seamless recovery or a protracted interruption.
Regulatory Compliance
For the sake of operational continuity and safety, several industries have passed legislation mandating the construction of backup power systems. In addition to being the law, following these rules is an excellent business practice that will boost a company's credibility and standing in the community.
Financial Impact
When the lights go out, it may have a devastating effect on the economy. Companies lose hundreds of dollars every minute due to downtime, particularly in areas where a lot is at stake, such as manufacturing and banking. To safeguard against these losses and keep operations running smoothly, standby power systems are an essential investment.
直接登录
创建新帐号