Key Components Involved
Understanding the intricacies of the buck topology necessitates a closer examination of its key components. The inductor, capacitor, and semiconductor switch form the trinity essential for its operation. The inductor serves as an energy storage element, managing the flow of current and facilitating the smooth transition of energy states. Capacitors act as reservoirs, smoothing voltage variations and contributing to overall stability. The semiconductor switch, typically a MOSFET, plays a pivotal role in controlling the energy transfer process. These components are described in greater detail below.
Inductor
Function: Serves as an energy storage device.
Operation: Stores energy during the switch's ON state and releases it during the OFF state.
Role: Governs the rate of change of current and influences the output voltage.
Figure 5: An Inductor
Capacitor
Function: Acts as a smoothing element.
Operation: Stores and releases charge to maintain a stable output voltage.
Role: Minimizes voltage ripple and contributes to overall system stability.
Figure 6: A Capacitor
Semiconductor Switch (MOSFET)
Function: Controls the flow of energy from the input source to the output.
Operation: Alternates between ON and OFF states, modulating the energy transfer process.
Role: Regulates the output voltage and determines the efficiency of the conversion process.
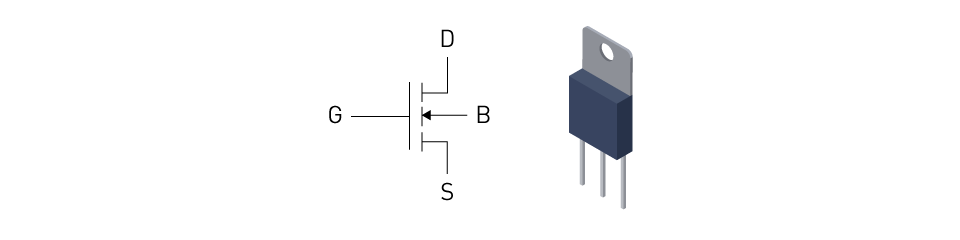
Figure 7: A MOSFET
直接登录
创建新帐号