Precision Positioning and Motion Control
Role of Stepper Motors in Precision Applications
The capacity of stepper motors to move in precise increments, also known as "steps," makes them an essential component in the field of precision positioning and motion control. This feature enables stepper motors to provide precise control over position, speed, and acceleration. Because of this one-of-a-kind quality, they are important in applications that call for high levels of accuracy and reproducibility.
In contrast to conventional motors, which are dependent on external sensors to ascertain their position, stepper motors are able to precisely control movement in a variety of applications without the application of feedback systems. The movement of a stepper motor is predictable, and each input pulse from the controller results in a known change in position. This is the reason why this is the case. By combining this predictability with the capability of operating in an open-loop system, it is possible to achieve precise control while simultaneously reducing complexity and eliminating costs.
Examples in Robotics, 3D Printing, and CNC Machinery
Robotics: Stepper motors are utilized in the field of robotics for the purpose of controlling the movement of robotic arms and actuators with a high degree of precision. It is possible for robots to carry out complex tasks such as assembling, picking and putting, and even surgery in the field of medical robotics because of the exact control that they have over their motion and location. For these applications, where accuracy and repeatability are of the utmost importance, stepper motors are an excellent choice because of their durability and their ability to provide exact control.
3D Printing: Stepper motors are an essential component of 3D printers since they are responsible for controlling the placement of the print head and the position of the platform. Because of the motor's capacity to carry out precise movements, it is possible to manufacture objects with exquisite details by layering them together gradually. Stepper motors play a crucial role in the development of 3D printing technology due to their direct impact on the quality and resolution of printed items.
CNC Machinery: Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machinery, which is utilized for cutting, milling, and drilling materials with a high degree of precision, is primarily dependent on stepper motors. These applications use stepper motors to control the movement of the tool and the workpiece. This gives the machine the ability to efficiently produce intricate patterns and designs with a high degree of precision. In order to achieve the tight tolerances that are necessary for CNC machining processes, the precision of the motors is absolutely necessary. This has a direct impact on the quality and precision of the items that are created.
Stepper Motors in the Semiconductor Industry
In the semiconductor sector, which is defined by its need for extreme precision and reliability, stepper motors are extensively relied upon for a variety of essential stages of the production and testing of semiconductors. When it comes to the operations that are involved in the fabrication of semiconductor devices, stepper motors are a vital component because of their distinctive characteristics, which include exact positioning, repeatability, and regulated movement characteristics.
Specific Uses in Semiconductor Fabrication and Testing
Wafer Handling and Positioning: Stepper motors are utilized in several pieces of machinery that are utilized for the purpose of handling and placing semiconductor wafers throughout the fabrication process. The exact movement and alignment of wafers under process equipment is made easier by them. This ensures that each wafer is oriented in the appropriate manner for processes such as photolithography, etching, and deposition.
Photolithography: Stepper motors are used in photolithography systems to operate the stage that holds the silicon wafer. This stage moves the wafer with sub-micron accuracy, which enables the precise patterning that is necessary to create microelectronic circuits. The capacity of stepper motors to carry out movements that are relatively small and incremental is absolutely necessary in order to accomplish the high resolution and patterning precision that are required in current semiconductor devices.
Inspection and Testing Equipment: Stepper motors are utilized in inspection and testing equipment after the fabrication process. These motors are utilized to move semiconductor devices under optical inspection instruments or to make exact electrical connections for the purpose of device testing. Because of their precision, inspection and testing may be carried out in an effective and precise manner, allowing for the correct identification of flaws or the verification of device functioning.
Case Studies Highlighting Precision and Control Benefits
One of the most noteworthy case studies is the application of stepper motors in a sophisticated photolithography instrument. In order to attain positioning accuracy of less than 10 nanometers, the stepper motors were coupled with a high-resolution feedback system. This made it possible to fabricate semiconductor devices with feature sizes that were far smaller than 100 nanometers. This level of precision was essential in pushing the bounds of Moore's Law, which made it possible to manufacture microprocessors that were both more powerful and more efficient in their use of renewable energy.
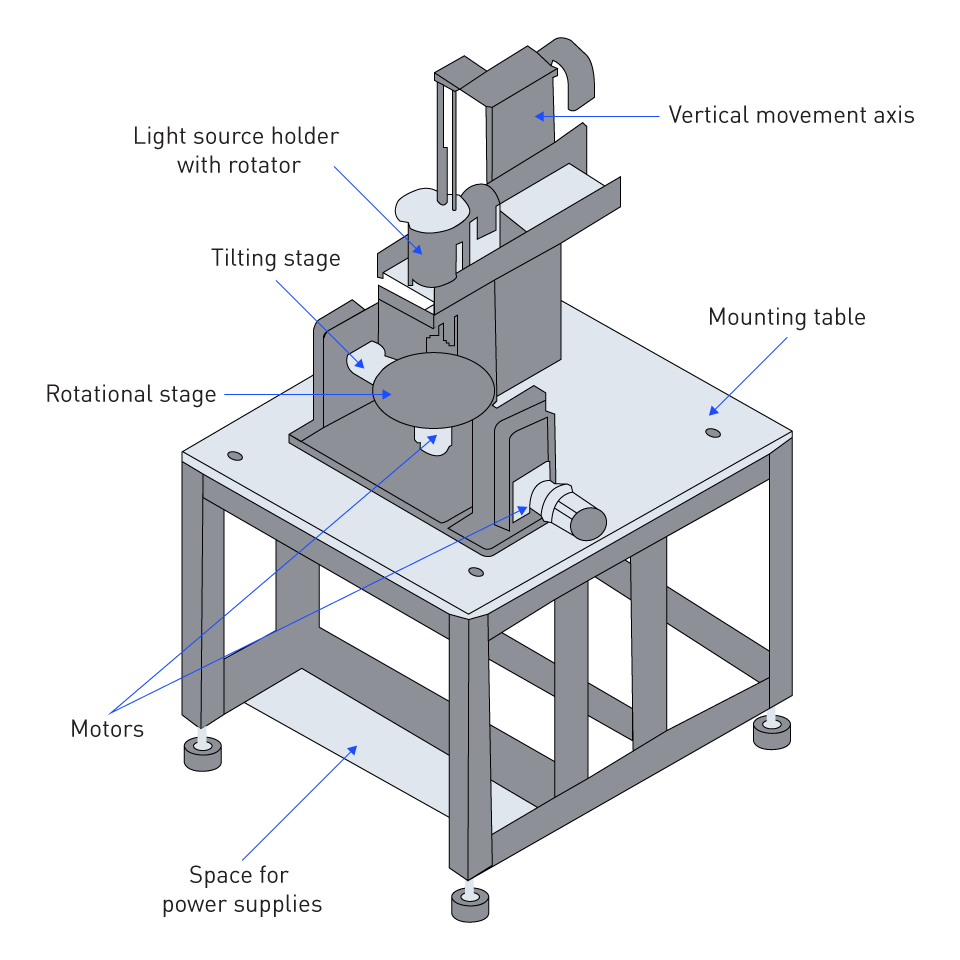
Figure 1: Stepper Motor Controlled Litography Equipment
Stepper motors are the subject of yet another case study that examines their application in automated wafer inspection systems. The high-precision stepper motors that were incorporated into these devices allowed them to scan entire wafers in a short amount of time, allowing them to identify flaws that were as small as a few nanometers wide. Not only did the utilization of stepper motors result in an increase in the throughput of the inspection process, but it also resulted in a considerable improvement in the detection accuracy, which ultimately led to an increase in the yields of semiconductor manufacture.

Figure 2: Stepper Motor Controlled Wafer Inspection System







直接登录
创建新帐号